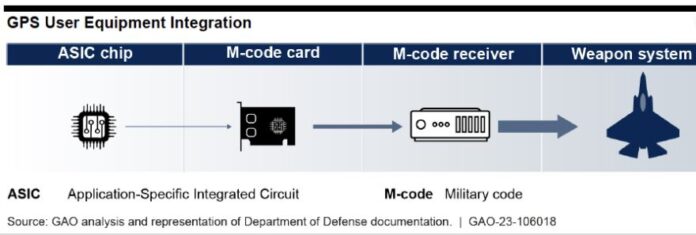
In a GPS modernization report released this week, the Government Accountability Office (GAO) said that the U.S. Space Force needs to develop a sound business case for new M-code capable handhelds. The agency also said that the service needs to assess the number of GPS satellites necessary to meet operational needs.
GAO, which said that the U.S. Defense Department agreed with both of its recommendations says the Space Force seeks to expand M-code technology use by developing a second increment that consists of an improved chip and card—and a handheld receiver. However, the organization contends that the Space Force lacks a committed customer for the handheld receiver.
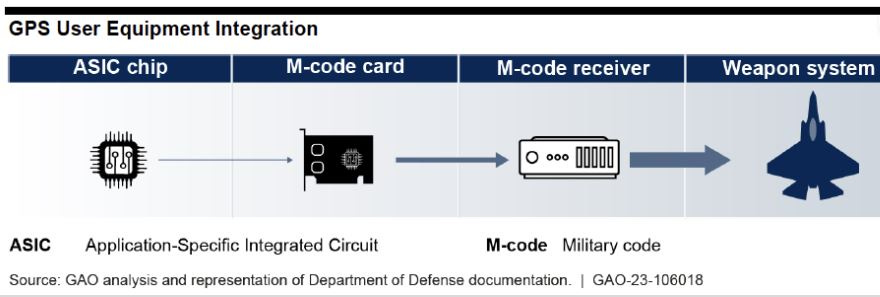
“The [U.S.] Army, the largest potential user of such a device, has its own plans for handheld receivers, and Marine Corps officials say the service is still considering its options,” according to the report. “Without a sound business case for its proposed handheld product, Space Force risks expending significant resources without providing a benefit to military users.”
The report said that while Space Force “seems well situated to achieve its approved requirement of keeping 24 M-code capable satellites in operation,” the service’s own analysis indicates that 27 satellites are necessary to meet real-world needs.
While not on the list of formal recommendations, GAO took a shot at the delays to the GPS Next Generation Operational Control System (OCX) program. “While Space Force has not finalized a new schedule for the program, officials acknowledged that the expected delays reflect slower-than- expected progress, and there are still risks to the program. If testing reveals additional deficiencies or any other unexpected issues arise, the program may delay the delivery further because little margin remains in the proposed schedule,” the report said.